As a general rule, The color of a rabbit is determined by the presence or absence of pigment in skin and hair. This can be broken down into three main groups: albino, black-eyed white, and all other colors. All other colors are broken down into “red” (agouti), “blue” (dilute), and “chocolate brown” (buckskin). The following article will discuss these different types of rabbits and how they get their fur color.
Rabbit Color Genetics – What is a Rabbit’s Color determined by?
The amount of black or yellow pigment present in a rabbit’s hair determines its color, which can vary from hair to hair and over the length of a single hair. On a single hair of a rabbit, there can be as many as five different bands of color.
Genetics of Rabbit Color – Most animals also have two types of hair: ‘outer’ guard hairs that are stiffer, thicker, and more commonly straighter than the finer, wavier, and softer undercoat hairs that are found on most other animals. The animal is protected by its outer coat, which is made up of guard hairs, while the undercoat acts as an insulator.Rabbit Color Genetics

What are the Rabbit Coat Color Genes?
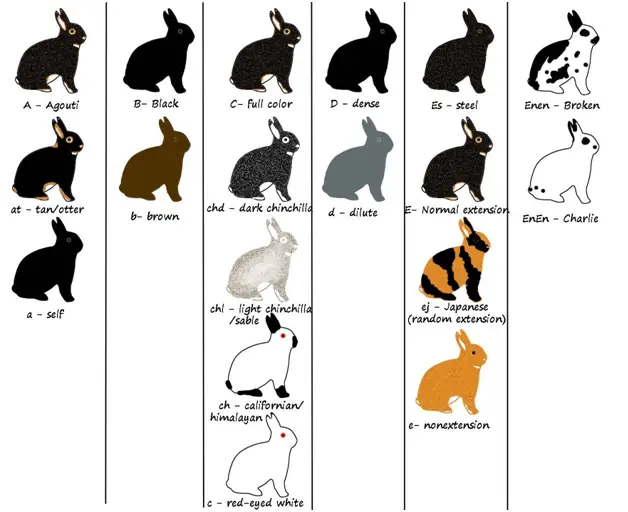
The fundamentals of rabbit coat color genetics are based on just FIVE basic genes, or chromosomal positions (loci), that code for the color of the rabbit’s coat. These genes are labeled with the letters A, B, C, D, and E, which makes logical sense.
The five gene loci have an effect on the TWO fundamental colors of a rabbit’s coat – black and yellow – by altering the way in which those two pigments are produced in the rabbit’s hair.
In addition, these five genes are influenced by other modifying genes, rufus factors, plus-and-minus modifiers, among other things.
It is possible to create practically hundreds of distinct bunny colors by combining all of the interactions and modifiers available.
Some genes cause the color to be produced, whereas other genes prevent color from being produced.
Here are the five basic rabbit coat color genes:
- Agouti hair shaft pattern (or not)
- Back (or chocolate)
- Complete color (or shaded, or albino)
- Dense (or dilute) color
- Extension of color (or its elimination or limitation)
What are the Dominant Genes?
This means that the dominant gene is “expressed,” meaning that you can observe its( dominant gene )influence on the color of the rabbit. The other gene is not expressed in any way. In fact, it’s possible that you won’t even know it’s there till it’s handed on to a child and coupled with another recessive mutation.

For example:
The agouti coloring is the most prominent. Consider the use of chestnut agouti in Netherland Dwarfs or castor in Rex rabbits as examples. Both of them are agouti. Because the agouti gene is dominant, only one agouti gene is required to generate an Agouti rabbit.
What are the Recessive Genes? ( recessive gene )
Solid black coloring (sometimes known as self-color) is recessive. The rabbit must have acquired two recessive solid-coloration genes, one from each of its parents, in order for it to develop a black coat. The agouti gene cannot be found in a black rabbit because if it were found, the rabbit would be agouti in the first place.
What is a Rabbit Color Breeding Chart? Or What is a rabbit Color Genetics Chart?
The rabbit color breeding chart shows the different color variations in rabbits. It may vary depending upon the breed and dominant and recessive genes. The general rabbit breeding chart is given below:
What are Rabbit Genotypes?
Each genotype a rabbit possesses comprises two factors, a dominant trait and a recessive trait, which work together to produce the genotype. Each parent will pass on one variable from their pair to their offspring when rabbits are bred in a laboratory. As a result, the kid will have its own gene that has variations from both the mother and father.
What is the Genotype of a Black Bunny?
If a rabbit is a black color, then its genotype is either “BB” or “Bb.” Always keep in mind that, despite the fact that the rabbit is black, it may still possess a chocolate gene, which it might pass on to its offspring.
What is the Actual Genotype of a Heterozygous Rabbit?
According to the rule of dominance, a trait is represented by two opposing factors of a gene in a heterozygous individual. Still, a trait is represented by two identical gene factors in a homozygous individual and vice versa.
In this case, the genotype of the heterozygous rabbit will be Bb, but the genotype of the homozygous recessive rabbit will be bb. The law of segregation says that the two components for a characteristic, which are present together in a heterozygous person (Bb), do not mix and are instead separated and supplied separately during gametogenesis, as opposed to the other way around.
As a result, the heterozygous person produces two types of gametes: half of the gametes with the letter “B” and half of the gametes with the letter “b.” The homozygous recessive person will only produce gametes that have the “b” gene.
What is the Genotype for a White Rabbit?
Pure-breeding albino/white rabbit has the genotype bb.

How does the Genetics of Rabbits Work?
How do Rabbits Pass on their Genetics?
To their offspring, each parent gives one of a pair of genes from each type of gene that they have. Each gene is represented by two copies in the progeny, one from each parent.
In the rabbit, dominant genes are expressed (as seen by the rabbit’s physical characteristics), while recessive genes are carried, with the possibility of being passed on to children. Regardless of whether it has a dominant or recessive trait, each gene is passed on to approximately half of the kids in each generation.
What is a Rabbit Color Genetics Calculator?
Rabbit color genetics calculator is an online tool used to predict the color of offspring depending upon their parents’ phenotypes/colors. It is available free on many websites.
The colors and patterns in rabbits – Breeds with Unique Colors and Patterns
Pet rabbits may be purchased in a variety of coat colors, which can be overwhelming at times. The fundamental color descriptions or color groupings that can be found in pet rabbits are covered in the following list. It is possible that not all pet rabbit breeds will come in all of these colors or patterns.
Possible Rabbit Colors
- Gray
- Light gray
- Pointed white
- Red
- Lilac
- Black otter
- Agouti
- Californian
- Chocolate steel
- Sable
- Chocolate tortoiseshell
- Black
- Blue
- Blue steel
- Blue tortoiseshell
- Broken
- Brown-gray agouti
- Castor
- Lilac chinchilla
- Lilac steel
- Fawn
- Blue otter
- Chinchilla
- Cinnamon
- Chocolate
- Chocolate agouti
- Chocolate chinchilla
- Copper agouti
- Cream
- Frosted pearl
- Sable marten
- Sable point
- Sandy
- Self-group
- Shaded group
- Lilac tortoiseshell
- Tri-colored
- Opal agouti
- Orange
- Pearl
- Tan Pattern
- Ticking
- Tortoise
- Silver or silver fox
- Tortoiseshell
- Silver Marten
Some rabbit colors are more challenging to come by than others, such as the silver and lilac colors, while others are more common at pet stores, such as the white and cream hues.
What is the Dominant Fur Color in Rabbits?
Black is the dominant fur color in rabbits
What is the Rarest Rabbit Color?
There is no obvious answer since there is no count of which colors are the most frequent or rarest around the rabbit world.
In contrast, if a rabbit possessed every recessive mutation presently known at the same time, except albinism and blue-eyed white since they would “cover” the others, they would be known as a Lilac Tortoise Himalayan.
There would be mutations in every gene in this rabbit, resulting in bleached pigments, yellow, blue, and brown hair strands, as well as unicolor hair strands. Such a rabbit has never been seen in person or on film, but it may exist somewhere in the world!

Common Misconceptions about rabbit coloration
Why do rabbits Change Fur Color?
Color changes in rabbits are an evolutionary survival mechanism that has developed due to their role as prey animals. Rabbits molt multiple times a year, usually in the spring and fall.
In the beginning, their fur changes color and then returns to its original color, effectively camouflaging them from possible predators. The only time you should be anxious is if your rabbit’s fur is becoming yellow, which can be caused by urine staining and should be avoided.
Why do some Breeds have more than one Color or Pattern Option available to them?
This is due to multiple allele responses. Skin color is a polygenic trait, and many genes play a role in it. When multiple alleles control skin color traits, there is a variation at different points, leading to more than one color or pattern option available to them.
18 Ways to Make Money by Rabbit Farming—Extensive Guidelines for Rabbit Farmers
Final Thoughts
When it comes to a rabbit’s hair, the amount of black or yellow pigment that is present affects the color, which can change from one hair to another as well as across the length of a single fiber of hair. Depending on the species, a single rabbit hair might have as many as five distinct bands of color on it.
In order to understand the genetics of rabbit coat color, it is necessary to understand just FIVE basic genes, also known as chromosomal locations (loci), that code for the color of the rabbit’s fur. These genes are designated with the letters A, B, C, D, and E, which makes logical sense given their location on the chromosome.